Mesh Compare Tool
Function Overview:
The Mesh Compare Tool is used to compare two 3D mesh files, typically for evaluating differences between scans—such as before and after modifications, or between design and final output. It highlights deviations in surface geometry with visual color mapping, helping users assess accuracy and consistency.
Recommended Applications:
- Supports comparison of morphological changes before and after treatment.
- Supports importing external STL files (Dental Laboratory Scanner Data) as a reference for accuracy verification.
Quick Steps:
- Select a case to enter the Mesh Compare Tool.
- Choose the two dental models you want to compare.
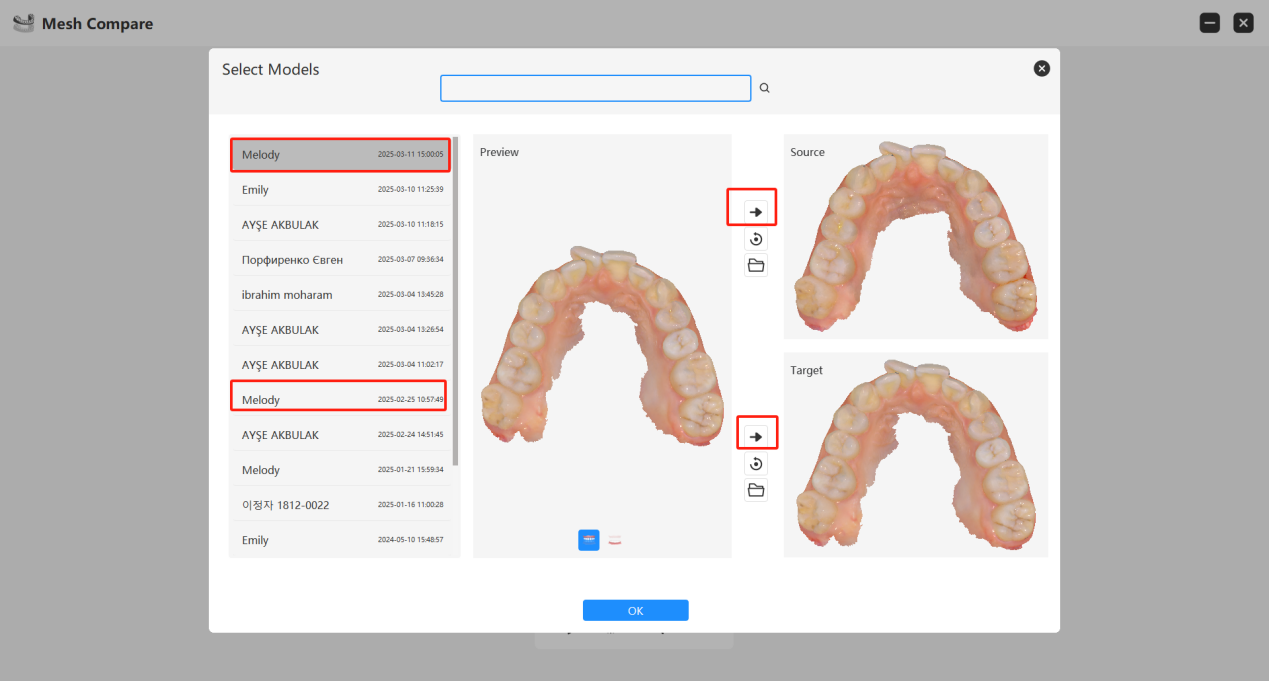
- Proceed with the comparison.
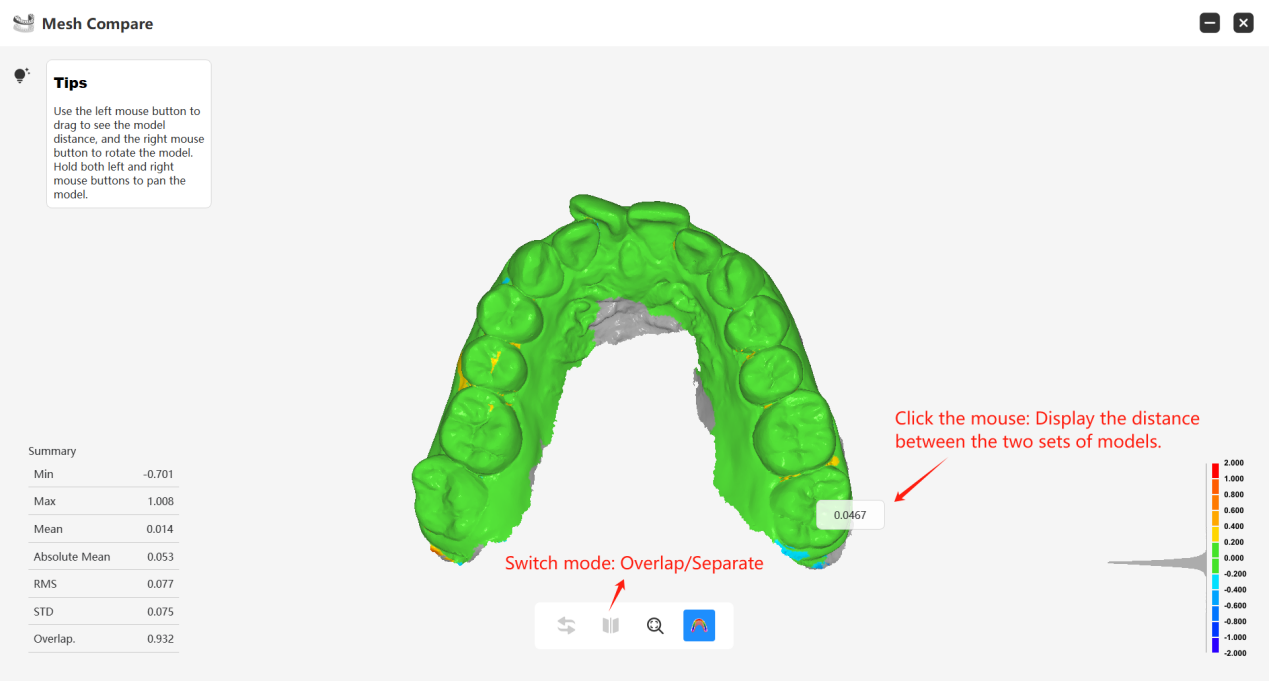
Meaning of Different Parameters in Mesh Compare Tool:
Min: The largest negative deviation value.
Max: The largest positive deviation value.
Mean (Average Value): The average of all the deviation values.
Absolute Mean (Absolute Average Value): The average of the absolute deviations.
RMS (root mean square): The square root of means of squares of deviation values.
STD (standard deviation): A statistic that measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean and is calculated as the square root of the variance. The standard deviation represents the distribution's dispersion. The curve with the smallest standard deviation has a high peak and a narrow spread, whereas the curve with the largest standard deviation is flatter and wider. When comparing various data sets, a lower standard deviation value indicates that the data are closer together.
Overlap.: Indicates the percentage of overlapping areas between two meshes within a certain error threshold. A higher value suggests a better match between the two meshes.